Body of Research
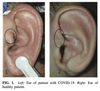
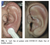
An Auricular Marker for COVID-19. Citation: (Volf 2020, 174)
In response to COVID-19 cases requiring mechanical ventilation, the chief of the intensive care unit of the Saint Antoine Paris Hospital in France was interested if acupuncture might help reduce the dosage necessary for the induction of anesthesia required for intubation, as suggested by several published articles. In response to this call from the hospital, the Scientific Acupuncture Department of the Paris XI University cared for 34 patients with severe COVID-19 to research a specific point...
Non-invasive Auricular Vagus Nerve Stimulation as a Potential Treatment for Covid19-Originated Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome. Citation: (Kaniusas 2020)
COVID-19 is an infectious disease caused by an invasion of the alveolar epithelial cells by coronavirus 19. The most severe outcome of the disease is the Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS) combined with hypoxemia and cardiovascular damage. ARDS and co-morbidities are associated with inflammatory cytokine storms, sympathetic hyperactivity, and respiratory dysfunction. The authors present and justify a novel potential treatment for Covid19-originated ARDS and associated co-morbidities, ...
Closed-loop bioelectronic medicine for diabetes management. Citation: (Gonzalez, 2020)
Research in neuromodulation has led to new therapeutic approaches to advance the field of bioelectronic medicine. Bioelectronic medicine exploits the fact that every organ in our bodies is neurally innervated and thus electrical interfacing with peripheral nerves can be a potential pathway for diagnosing or treating diseases such as diabetes. Aspects of this medicine share similarities to the theoretical concepts of clinical acupuncture, and align with research in neuro-auricular modulation (...
Review of Transcutaneous Vagus Nerve Stimulation: Challenges for Translation to Clinical Practice. Citation: (Yap 2020)
Several studies investigating the use of transcutaneous vagus nerve stimulation (tVNS) for disorders tinnitus, migraine and pain show therapeutic effects similar to those produced by the more invasive direct vagus nerve stimulation (VNS). Although VNS is an FDA-approved therapy for the treatment of both depression and epilepsy, it is limited to being a second or third-line treatment option for severe, intervention-resistant cases, due to risks involved with device implantation. In contrast, t...
Neural networks and the anti-inflammatory effect of transcutaneous auricular vagus nerve stimulation in depression. Citation: (Liu, 2020)
Review article on the potential of transcutaneous auricular vagus nerve stimulation (taVNS) in managing depression — and as it possibly relates to pain and other chronic conditions affected by negative emotional affect and psychological conditions such as depression.
Reference: Liu, CH., Yang, MH., Zhang, GZ. et al. Neural networks and the anti-inflammatory effect of transcutaneous auricular vagus nerve stimulation in depression. J Neuroinflammation 17, 54 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1186/s1...
Chronic inflammation in the etiology of disease across the life span. Citation: (Furman, 2019)
Chronic inflammatory diseases have been recognized as the most significant cause of death in the world today, with more than 50% of all deaths being attributable to inflammation-related diseases such as ischemic heart disease, stroke, cancer, diabetes mellitus, chronic kidney disease, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and autoimmune and neurodegenerative conditions[2]. Evidence is emerging that the risk of developing chronic inflammation can be traced back to early development, and i...
The anatomical basis for transcutaneous auricular vagus nerve stimulation. Citation: (Butt 2019)
Our metabolic functions (e.g. organs, glands, involuntary muscles) are influenced by the autonomic nervous system (ANS) via sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions. The vagus nerve, the 10th longest of the cranial nerves, is a major component of the parasympathetic nervous system and serves to maintain homeostasis providing bidirectional communication between the body and brain.
The neuroatanomy of the auricular branch of the vagus nerve (ABVN) offers insight for an understanding of the ef...
Current Directions in the Auricular Vagus Nerve Stimulation I – A Physiological Perspective. Citation: (Kaniuses, 2019)
The only place on the body where the vagus nerve (VN) sends its only peripheral branch is on the outer ear. The auricle is where this VN branch surfaces to form a cutaneous receptive field in the pinna of the ear — an area responsive to peripheral nerve stimulation. Thus, the auricle allows for easy access for auricular (and transcutaneous auricular) vagus nerve stimulation (aVNS/taVNS), that relays the stimuli to the brainstem and higher brain regions via extensive projections to second and...
Current Directions in the Auricular Vagus Nerve Stimulation II – An Engineering Perspective. Citation: (Kaniusas 2019, 772)
Bioelectronic medicine progressively comes into focus as offering a non-pharmaceutical treatment option for various diseases. Here neuromodulation of the vagus nerve (VN) has gained a special interest. In a comprehensive review technical issues, modeling concepts, regulatory and safety requirements, and novel architectures of open and closed-loop aVNS paradigms, Kaniusas and his colleagues focus on the physiological role of VN including a biology-driven rationale for Auricular Vagus Nerve Sti...
Peripheral effects of vagus nerve stimulation on anxiety and extinction of conditioned fear in rats. Citation: (Noble 2019)
Vagus nerve stimulation (VNS) has been shown to enhance extinction of conditioned fear in rats. Previous findings support this finding. It is hypothesized that this is the result of enhanced consolidation of extinction memories through the promotion of plasticity in related neural pathways. There are other explanations as well. The work supports rapidly expanding research into VNS, both invasive VNS and transcutaneous VNS (which is most often applied at the ear, e.g. transcutaneous auricular ...
The Present and Future of Vagus Nerve Stimulation. Citation: (Yang 2019, 344-352)
Vagus nerve stimulation (VNS) is an adjunctive neuromodulation therapy that was approved in 1997 for the alleviation of seizures; however, efforts to control epilepsy by stimulating the vagus nerve have been studied for over 100 years. The ability for VNS to affect various brain areas, has a wide indication for various intractable epileptic syndromes and epilepsyrelated comorbidities. Moreover, recent studies have shown anti-inflammatory effects of VNS, and the indication is expanding beyond ...
Experimental Results in Auricular Medicine—A New Hypothesis. Citation: (Litscher 2018, 132)
This editorial proposes a multimodal concept for future research on the Vascular Autonomic Signal (VAS) through hypothesis concerning mechanisms of the VAS. Download the paper on Medicines (external link)
Litscher G, Yannacopoulos T, Kreisl P. Nogier Reflex: Physiological and Experimental Results in Auricular Medicine—A New Hypothesis. Medicines 2018;5(4):132.